What is Bio-Economy?
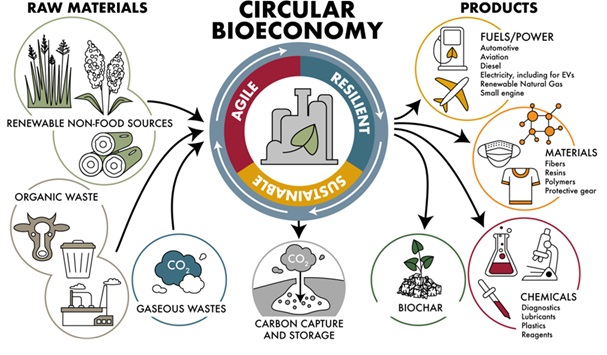
- Bio-economy refers to the knowledge-based production and utilization of biological resources, such as plants, animals, micro-organisms, and related processes, to generate sustainable goods and services.
- It involves the application of biotechnology, bioengineering, and other scientific advancements to address economic, environmental, and societal needs across various sectors.
- The bio-economy supports sustainable growth by utilizing renewable biological resources, reducing dependence on fossil fuels, and minimizing environmental impact.
Key Sectors of Bio-Economy
- Bio-industrial Sector: Includes industries that use biotechnology for producing biofuels, biodegradable plastics, bio-based chemicals, and more.
- Bio-pharma Sector: Focuses on the production of pharmaceuticals, vaccines, and medical devices using biological methods.
- Bio-agriculture: Involves the use of biotechnology for improving agricultural productivity, pest control, and food security.
- Environmental Biotechnology: Focuses on waste management, pollution control, and bioremediation.
Importance of Bio-Economy
- Environmental Sustainability: By using biological resources, bio-economy reduces dependency on fossil fuels, decreases carbon emissions, and helps combat climate change.
- Economic Growth: Promotes the development of new industries, boosts innovation in biotechnology, and creates employment opportunities.
- Circular Economy: Promotes a model that emphasizes recycling and the efficient use of resources, contributing to a sustainable future.
Bio-Economy in India: Current Status and Growth
- India’s bio-economy has witnessed impressive growth over the past decade, evolving into a key contributor to the national economy.
- The sector has been growing at a rapid pace, supported by technological innovations, government policies, and increasing global demand for sustainable solutions.
Key Statistics
- Market Growth: India’s bio-economy was valued at around $10 billion in 2014. By 2024, this figure is projected to exceed $130 billion.
- Contribution to GDP: Bio-economy contributes about 4% to India’s GDP, reflecting its growing importance in the national economy.
- Global Ranking: India ranks 12th globally in terms of bio-manufacturing, demonstrating its leadership in the biotech and bio-manufacturing industries.
- Challenges in Bio-Economy: Despite rapid growth, India’s bio-economy faces several challenges:
- Regulatory Hurdles: The regulatory framework for biotechnology needs to be streamlined to promote innovation while ensuring safety and environmental standards.
- Investment Needs: Continued investment in research, development, and infrastructure is essential for further growth and global competitiveness.
- Awareness and Education: Increasing awareness about bio-based products and their benefits is crucial to drive adoption across industries.
Government Initiatives to Boost Bio-Economy
- The Indian government has introduced several policies and initiatives to promote bio-economy growth:
Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC):
- BIRAC plays a critical role in supporting the biotechnology ecosystem in India. It offers funding, mentorship, and infrastructure for start-ups and research institutions.
- Key initiatives include the Biotechnology Ignition Grant (BIG) and BioNEST, which provide support to innovative biotech start-ups.
National Biofuel Policy (2018):
- This policy aims to promote the use of biofuels, such as ethanol, biodiesel, and bio-gas, in various sectors, including transportation, energy, and agriculture.
- It supports the development of sustainable, renewable energy sources, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
National Bio-pharma Mission:
- The mission aims to enhance India’s capacity in the biopharmaceutical sector, focusing on the production of affordable medicines, vaccines, and diagnostics.
- It supports the development of indigenous biologics and bio-similars, ensuring access to healthcare for all.
National Mission on Bio-economy:
- A comprehensive policy that supports research, innovation, and the commercialization of biotechnology. It focuses on expanding India’s bio-manufacturing capacity and positioning the country as a leader in bio-based products.
Biological Research Regulatory Approval Portal (BioRRAP):
- Launched as a single-window platform, BioRRAP facilitates the approval process for research related to biological resources.
- It streamlines regulatory approvals, reducing delays and fostering innovation in the biotech sector.
Future Prospects and Opportunities
- India’s bio-economy is expected to continue expanding, driven by the following trends:
- Increased Biotech Innovation: Continued research in bioengineering, genetic modification, and sustainable production methods will drive growth in the agriculture and pharmaceutical sectors.
- Bio-manufacturing: The shift towards bio-based chemicals and materials will lead to a reduced environmental footprint, contributing to global sustainability goals.
- Global Market Expansion: India is poised to become a global leader in biotechnology, with increasing opportunities in bio-pharma, biofuels, and bio-agriculture.
Future Projections:
- By 2030, India’s bio-economy is expected to be valued at around $300 billion, further strengthening its role in global bio-manufacturing and sustainable development.
Frequently asked questions in the exam.
Q. What is the current size of India’s Bio-Economy?
It has grown from $10 billion in 2014 to over $130 billion in 2024, with projections of $300 billion by 2030.
Q. What is the National Bio-Economy Mission?
It is a proposed mission to support innovation, manufacturing, and commercialization in the bio-economy space, aligning with India’s sustainable development goals.
Q. What is BioRRAP?
The Biological Research Regulatory Approval Portal (BioRRAP) is a single-window online system to streamline regulatory approvals for biological research.


