

| GS Paper -III : Environment and Ecology |
|
Feature |
Description |
|
Date of Enforcement |
1 June 1961 |
|
Signing Venue |
Washington, D.C. |
|
Original Signatories |
12 countries – USA, USSR, UK, France, Norway, Australia, New Zealand, Argentina, Chile, Japan, Belgium, South Africa |
|
Current Members |
57 (29 Consultative + 28 Non-Consultative) |
|
India’s Membership |
1983 (as Consultative Party) |
|
Geographical Scope |
Entire region south of 60°S latitude |
A multi-layered legal framework evolved from the treaty:
|
Threat |
Impact |
|
Climate Change |
Rapid ice-sheet melting; rising sea levels |
|
Ocean Acidification |
Negative impact on marine biodiversity |
|
Human Activities |
Pollution from research stations |
|
Tourism |
Over-tourism causing ecological imbalance |
|
Fishing |
Over-harvesting of krill disrupts food chain |
|
Year |
Initiative |
|
1981 |
First Indian Antarctic Expedition |
|
1983 |
Dakshin Gangotri Station (now inactive) |
|
1989 |
Maitri Station – permanent research center |
|
2012 |
Bharati Station – modern multidisciplinary facility |
|
2022 |
Indian Antarctic Act, 2022 – legal framework for Indian activities |
|
2024 (Planned) |
Maitri-II Station – new research center |
|
Challenge |
Description |
|
Pressure for Resource Exploitation |
Future mining or energy exploration may increase |
|
Tourism Regulation |
Over 100,000 tourists in 2024 – environmental risk |
|
Conflicting Interests |
Rising presence of China & Russia creates tension |
|
Insufficient Climate Measures |
Current protocols lack binding emission reductions |
| GS paper -III energy and environment |
Geothermal energy is the heat energy stored within the Earth. The term “Geo + Thermal” literally means “Earth + Heat.” This energy flows from the Earth’s core to its surface, primarily generated by the decay of radioactive elements (Uranium, Thorium, Potassium) and residual heat from the Earth’s formation. It can be used for electricity generation, heating, agriculture, and industrial applications.
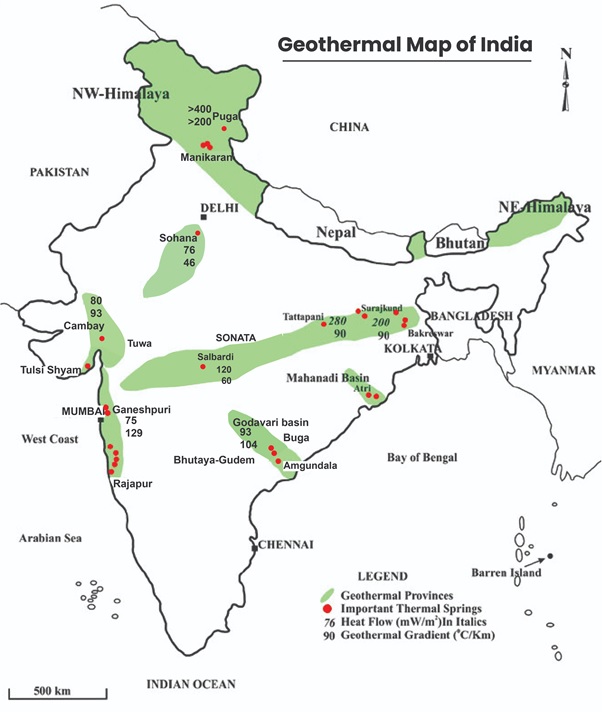
Geothermal energy technology harnesses underground heat, available as hot water or steam, to drive turbines and generate electricity.
India has immense geothermal potential, offering a clean, sustainable, and reliable energy source. With coordinated efforts by government, industry, and research institutions, focusing on technical feasibility, environmental safety, and infrastructure, geothermal energy can significantly contribute to India’s energy diversification and net-zero emission targets.

Our support team will be happy to assist you!
