Prelims: (Science & Technology + CA)
Mains: (GS-3 – Science & Technology) |
Why in the News?
Scientists at ICAR–Central Rice Research Institute (CRRI), Cuttack have developed a new indigenous genome-editing platform using TnpB proteins, offering a compact, low-cost and IP-free alternative to globally patented CRISPR-Cas systems.
Separately, CSIR–Institute of Genomics & Integrative Biology (IGIB) has developed “BIRSA 101”, India’s first indigenous CRISPR-based gene therapy for Sickle Cell Disease, marking a major advancement in Indian genomic medicine.
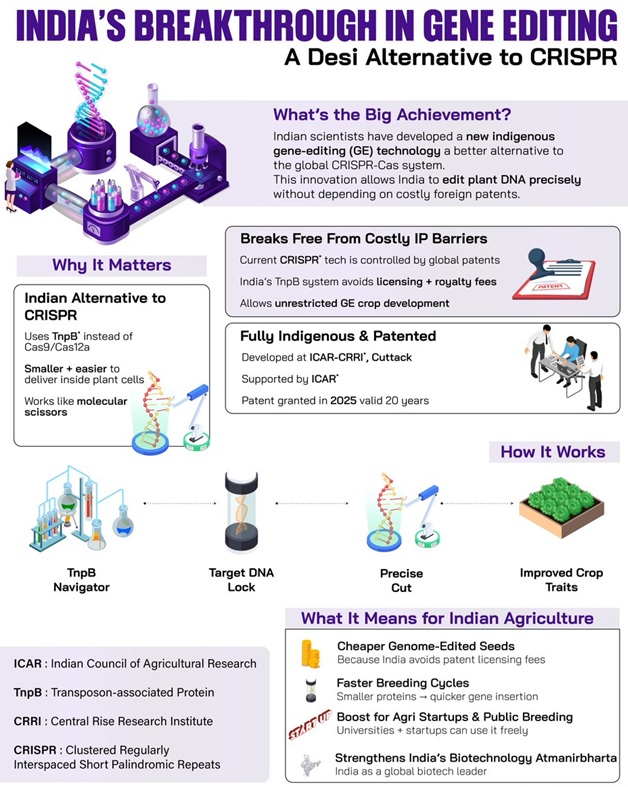
India’s Indigenous TnpB-Based Genome Editing Tool
Overview
- Developed using TnpB (Transposon-associated proteins) instead of widely used CRISPR-Cas9 or Cas12a systems.
- TnpB functions as a miniature molecular scissor, capable of precise DNA cuts and edits in plants.
Why TnpB Is a Breakthrough
- Extremely small enzyme size:
- TnpB ~ 408 amino acids
- Cas9 ~ 1,000–1,400 amino acids
- Cas12a ~ 1,300 amino acids
- Smaller size allows:
- Easier delivery into plant cells
- Reduced dependence on complex tissue-culture steps
- More efficient genome editing in crops
Significance
- Reduces India’s dependence on foreign CRISPR patents held by entities like the Broad Institute and Corteva.
- Enables affordable, commercial genome-edited (GE) crops without paying heavy licensing fees.
- Strengthens Atmanirbhar Bharat in agri-biotechnology and provides India technological sovereignty over next-generation gene-editing tools.
- Addresses long-standing concerns that global biotech tools are dominated by foreign multinationals.
What is BIRSA 101?
Overview
- BIRSA 101 is a precise gene-editing therapy aimed at correcting the mutation responsible for Sickle Cell Disease.
- Named in honour of Bhagwan Birsa Munda, recognising the high prevalence of the disease among India’s tribal communities.
Scientific Basis
- Uses enFnCas9 (enhanced Francisella novicida Cas9), an Indian-engineered and optimised CRISPR platform developed by IGIB.
Significance
- Provides a low-cost alternative to global gene therapies like Casgevy, priced at ~USD 2.2 million.
- Technology transferred to the Serum Institute of India for large-scale, affordable deployment.
- Represents a major step toward achieving a Sickle Cell–Free India by 2047.
- Strengthens India’s position in genomic medicine, gene therapy innovation, and self-reliant healthcare.
What is Genome Editing?
Overview
Genome editing refers to technologies (such as CRISPR) that enable scientists to precisely cut, modify, or replace specific DNA sequences within an organism.
Key Features
- Creates targeted mutations in existing genes
- Does not introduce foreign DNA (unlike GM crops)
- Allows high-precision genetic modifications
How CRISPR Works
- Uses a guide RNA (gRNA) to locate a specific DNA sequence
- Directs a Cas enzyme (Cas9 or Cas12a) to that site
- Cas enzyme acts as a molecular scissor, cutting the DNA
- The cell repairs the break, enabling:
- Gene knockout
- Mutation correction
- Gene insertion
Cas Enzyme Variants
- Cas9: Most commonly used for simple DNA cuts
- Cas12a: Offers higher precision, different guide RNA structure, and broader editing possibilities
Applications of Genome Editing
Medicine
- Treatment of genetic disorders
- Development of gene therapies (e.g., sickle cell disease)
- Personalised medicine
Agriculture
- Climate-resilient crops
- Higher-yield and disease-resistant varieties
- Reduced chemical dependence
Scientific Research
- Gene function studies
- Development of biological tools
- Advancements in synthetic biology
Significance of These Breakthroughs
- Strengthens India’s biotech independence
- Reduces reliance on foreign patented technologies
- Enables low-cost gene therapy solutions
- Boosts agricultural innovation and GE crop development
- Positions India as a leader in affordable genomic medicine
FAQs
1. What is the TnpB-based editing tool?
A compact, indigenous gene-editing system using TnpB proteins that can precisely cut DNA and serves as an alternative to CRISPR systems.
2. Why is TnpB important for India?
It is IP-free, low-cost, and independent of foreign patents, enabling affordable genome editing in crops.
3. What is BIRSA 101?
India’s first indigenous CRISPR-based therapy for Sickle Cell Disease using the enFnCas9 platform.
4. How is CRISPR different from TnpB?
CRISPR uses larger Cas enzymes (Cas9/Cas12a), while TnpB is a much smaller, easier-to-deliver protein.
5. What are the applications of genome editing?
Gene therapy, crop improvement, disease research, and biotechnology innovation.
|



