The world is rapidly moving toward advanced digital infrastructure, yet millions of people still live in areas where traditional fiber, cable, or mobile-tower–based internet cannot reach.
In such regions, Satellite Internet is emerging as a game-changing technology. Companies like Starlink (SpaceX) are deploying thousands of small satellites in Low Earth Orbit (LEO) to provide high-speed, global internet coverage.
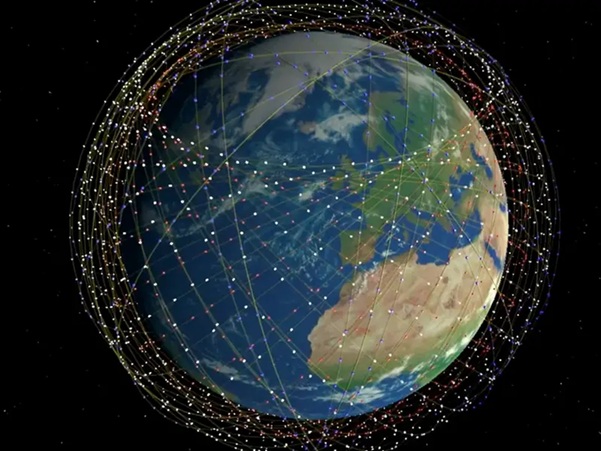
How Satellite Internet Works
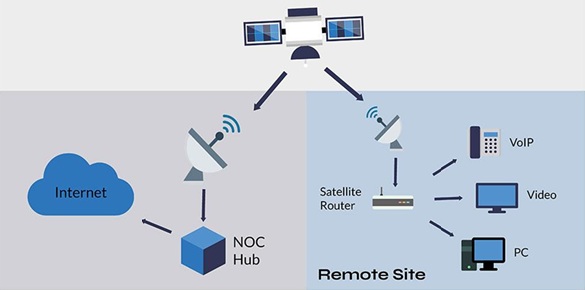
(Three-Link Architecture Model)
The basic architecture of satellite internet consists of three key components:
A. User Satellite Dish (User Terminal)
- Installed on rooftops or open areas
- Capable of both receiving and transmitting data
- Communicates directly with satellites through radio waves
B. Satellites (LEO / MEO / GEO)
- Route the data between the user and the internet
- Act as space-based relay nodes
C. Ground Stations / Data Centers
- Connected to the global internet backbone
- Process user requests (web pages, streaming, etc.) and send data back via satellites
Data Flow Process
- User Terminal → Satellite → Ground Station
- Ground Station → Satellite → User Terminal
Thus, the internet is delivered through a space-based relay network.
Why Is Satellite Internet Needed?
Limitations of Ground-Based Networks
- Extremely expensive and difficult to lay fiber/towers in remote or mountainous areas
- Forests, islands, deserts remain mostly unconnected
- Natural disasters can damage terrestrial infrastructure
- Temporary connectivity requirements (mining zones, defense, disaster response) are not feasible with traditional networks
How Satellite Systems Solve These Challenges
- Space-based coverage enables connectivity anywhere on Earth
- Network remains operational even during disasters
- Helps bridge the global digital divide
- Ensures equitable connectivity in both dense cities and isolated locations
Types of Satellite Orbits for Internet
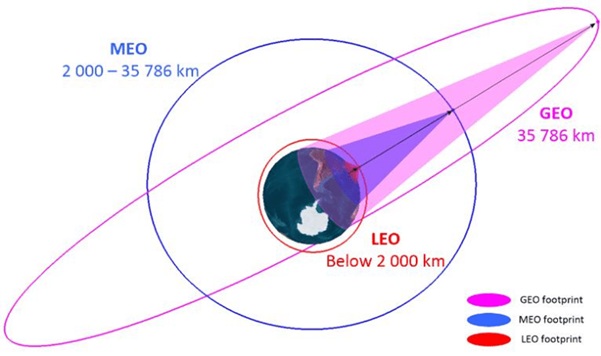
|
Feature
|
GEO
|
MEO
|
LEO
|
|
Altitude
|
35,786 km
|
2,000–35,786 km
|
< 2,000 km
|
|
Latency
|
High (600–900 ms)
|
Medium (150–300 ms)
|
Very Low (20–40 ms)
|
|
Coverage
|
Very large (3 satellites cover globe)
|
Medium
|
Small (requires thousands)
|
|
Examples
|
Viasat, Inmarsat
|
O3b
|
Starlink, OneWeb
|
LEO is preferred for high-speed, low-latency internet. Starlink currently has 7,000+ satellites in operation (aim: 42,000).
Advantages and Disadvantages of Satellite Internet
Advantages
- Connectivity in remote & inaccessible areas
- Mountains, oceans, deserts, forests — everywhere.
- Highly resilient during disasters
- Less affected by floods, earthquakes, and storms.
- On-demand deployment
- Useful in defense, emergency response, expeditions.
- Competition is driving better speeds and lower costs
- (Starlink, OneWeb, Amazon Kuiper)
Disadvantages
- High user-terminal cost (dish + router)
- Latency issues with GEO/MEO systems
- Space debris concerns: Risk of satellite collisions increases
- High launch and maintenance expenses: Especially with large constellations
Conclusion
Satellite Internet is not just a technological innovation — it is a necessity for global digital inclusion. By providing reliable connectivity to underserved regions and ensuring network resilience during crises, it is poised to become a crucial part of the world’s communication ecosystem. As technology improves and more satellites are deployed, seamless internet everywhere may soon become a reality.



