(Preliminary Examination: Current Affairs)
(Mains, General Studies Paper 2: Bilateral, Regional, and Global Groupings and Agreements Relating to India and/or Affecting India's Interests) |
Context
On November 16, 2025, India's External Affairs Minister (EAM), Dr. S. Jaishankar, held a key meeting with Qatar's Prime Minister and Foreign Minister, Sheikh Mohammed bin Abdulrahman Al-Thani, in Doha. During the meeting, extensive discussions were held on bilateral relations, energy cooperation, trade, investment, and regional and global issues.

India-Qatar Dialogue: Key Outcomes
- Commitment to further strengthen their strategic partnership between the two countries
- Agreement to explore new opportunities to ensure stability in the energy sector, especially LNG supplies
- Emphasis on expanding trade and investment cooperation
- Shared vision for peace and stability in West Asia
- Promotion of people-to-people contacts, labor cooperation, and economic partnership
India-Qatar Bilateral Relations
Historical
- Relations between India and Qatar are based on centuries-old trade ties. Formal diplomatic relations were established in 1973.
- Over time, the two countries have become strong partners in energy, trade, investment, and security cooperation.
Trade
- India-Qatar bilateral trade stood at $14.08 billion in 2023-24.
- Qatar primarily exports LNG, LPG, petroleum products, and chemicals to India.
- India exports rice, marine products, steel, machinery, electronic goods, etc. to Qatar.
- Qatar is a major energy provider to India, and a large portion of India's LNG requirements come from Qatar.
Defense Relations
- There is a defense cooperation agreement between the two countries. The Indian Navy and the Qatari Navy conduct regular cooperation exercises.
- Intelligence sharing, maritime security, and counter-terrorism cooperation between the two countries have also strengthened.
Cultural Relations
- Approximately 850,000 Indians reside in Qatar, constituting its largest expatriate population.
- The Indian community plays a significant role in education, health, trade, and industry.
- There are close cultural ties between the two countries through art, music, sports, and cultural festivals.
Tourism
- Qatar is an emerging attraction for Indian tourists, especially Doha, the Pearl Qatar, and the Islamic Art Museum.
- Strong air connectivity between India and Qatar promotes both tourism and trade.
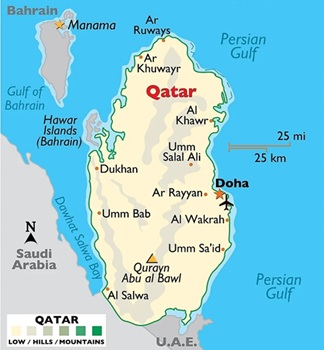
Qatar: Destinations
- Location:
- Located in the north-east of the Arabian Peninsula
- Bordered only by Saudi Arabia to the south
- Surrounded by the Persian Gulf on all sides.
- Maritime borders with Bahrain, the United Arab Emirates, and Iran
- Government: Constitutional Monarchy
- Ruler: Emir Tamim bin Hamad Al Thani
- Capital: Doha
- Official language: Arabic
- Currency: Qatari Riyal (QAR)
- Area: Approximately 11,571 square km.
- Climate: Hot desert climate (extreme heat, little rainfall)
- Prime Minister: Sheikh Mohammed bin Abdul Rahman Al-Thani
- Parliament: Shura Council
- Qatar is renowned for its "dependent foreign policy" and mediation roles.
- Developed country: One of the world's wealthiest countries
- Economy base:
- Liquefied natural gas (LNG)
- Natural gas and oil
- Qatar is considered one of the world's leading LNG exporters.
- It relies on a large number of foreign workers.
- It has the world's third-largest natural gas reserves (after Russia and Iran).
- North Field (Qatar): The world's largest gas field
- Qatar holds a global powerhouse status in energy security.
|




