(Prelims: Current Affairs)
(Mains, General Studies Paper 2: Impact of Policies and Politics of Developed and Developing Countries on India's Interests; Overseas Indians) |
Context
The India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) is an ambitious project designed to enhance economic and trade connectivity between India, the Middle East, and Europe. In recent years, especially following trade tensions with the United States, India has focused on diversifying its economic partnerships globally.
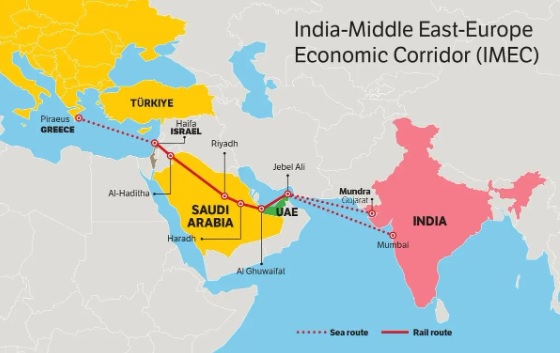
About IMEC
- The India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) is a multinational initiative launched during the G-20 Summit held in New Delhi in 2023.
- Its objective is to ensure seamless movement of goods, energy, and data to Europe through India, the United Arab Emirates (UAE), Saudi Arabia, Jordan, and Israel.
- This corridor integrates infrastructure such as sea ports, high-speed rail networks, clean hydrogen pipelines, and digital cables.
- It aims to make trade between India and Europe faster, cost-effective, and sustainable, while also strengthening economic cooperation with Middle Eastern countries.
Connectivity Routes
The IMEC route is designed to connect India with the Middle East and Europe:
- India: This corridor originates from ports on India's west coast, particularly in Gujarat (such as Mundra), from where goods are shipped by sea to the Middle East.
- United Arab Emirates (UAE): UAE ports (such as Jebel Ali) receive goods and send them via rail network to Saudi Arabia.
- Saudi Arabia: The rail network in Saudi Arabia carries goods to Jordan. It also provides access to clean hydrogen and power cables.
- Jordan: Jordan transports goods via rail network to the Israeli port of Haifa.
- Israel: From the Haifa port, goods travel by sea to Europe, especially Mediterranean countries (such as Italy and France).
- Europe: European ports transport goods to their final destinations and promote digital and energy connectivity.
Benefits
- Fast and cost-effective trade: IMEC reduces time and costs compared to traditional sea routes (such as the Suez Canal).
- Economic cooperation: Promotes trade and investment between India, the Middle East, and Europe, particularly strengthening the $136 billion India-EU trade.
- Infrastructure development: Upgrading ports, rail networks, and digital/energy cables accelerates regional development.
- Sustainable energy: Clean hydrogen pipelines and power cables promote environmentally friendly energy solutions.
- Geopolitical strategy: India has the opportunity to counter Pakistan's regional alliance strategies in the Middle East.
- Strong supply chain: It makes supply chains more resilient by reducing dependence on volatile regions like the Red Sea.
Impact
- Economic impact: IMEC will boost trade between India and Europe, especially for Mediterranean countries (such as Italy and France), which could be affected by the emergence of Arctic routes.
- Regional stability: Cooperation with countries like Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and Jordan will promote economic stability in West Asia.
- Global trade position: It will help establish India as a significant stakeholder in global trade, especially with a $4 trillion economy.
- Geopolitical significance: IMEC provides India with the opportunity to develop strong strategic partnerships with the Middle East and Europe that could influence the regional balance of power.
- Environmental impact: Sustainable measures like clean hydrogen and power cables support climate change goals.
Challenges
- Geopolitical instability: Tensions in West Asia, such as those between Israel and Arab countries, complicate IMEC implementation.
- Disruption in the Red Sea: Houthi attacks have disrupted trade routes, forcing goods to be transported via the Cape of Good Hope, increasing time and costs.
- The emergence of Arctic routes: Climate change is opening up new trade routes in the Arctic, which could pose challenges to Mediterranean countries.
- Financial and technical constraints: Rail, port, and digital/energy infrastructure require significant investment and technical expertise.
- Regional competition: The need to include other countries in the Middle East, such as Egypt or other Gulf countries, could complicate IMEC planning.
The way forward
- Flexible strategy: IMEC will need to adapt to geopolitical changes, such as the inclusion of additional ports and commercial centers in Saudi Arabia and Egypt.
- Enhancing Economic Cooperation: India should strengthen bilateral and multilateral agreements with the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and European countries.
- Infrastructure Investment: Long-term investments and international cooperation should be enhanced to upgrade ports, rail, and digital networks.
- Focus on Regional Stability: Promote stability in West Asia by supporting initiatives such as the Gaza Peace Plan.
- Exploring Alternative Routes: India should remain focused on Mediterranean routes while evaluating the potential of Arctic routes.
- Shared prosperity: India and Europe should pool resources to promote prosperity in the IMEC region, making the corridor an important link in global trade.



