Prelims: (Geography + CA)
Mains: (GS 1 – Physical Geography; GS 3 – Climate Change, Oceanography, Environmental Conservation) |
Why in News ?
Recent scientific studies have highlighted that the Southern Ocean absorbs a significant share of carbon dioxide released by human activities, thereby mitigating global surface warming and playing a crucial role in regulating Earth’s climate system.

Background & Context
Global warming driven by rising greenhouse gas emissions has intensified research on natural climate regulators, particularly oceans. While oceans collectively absorb over 90% of excess heat and about one-fourth of anthropogenic CO₂, the Southern Ocean’s contribution is disproportionately large compared to its surface area. Its unique circulation patterns, cold waters, and interaction with the atmosphere make it a critical carbon and heat sink, slowing the pace of global temperature rise.
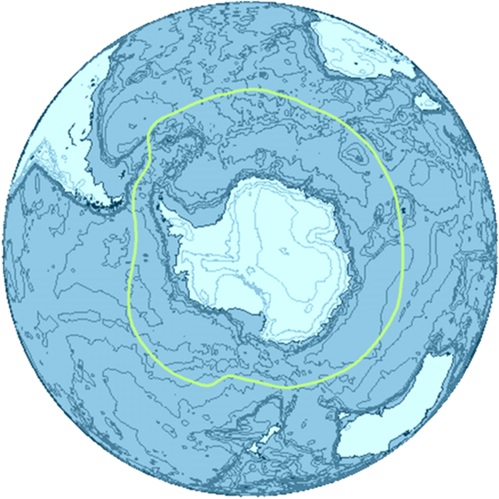
Southern Ocean: Key Facts
Location and Extent
- Also known as the Antarctic Ocean
- Fourth-largest ocean by surface area
- Defined by the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) as the southernmost part of the World Ocean
- Encircles Antarctica
- Connects the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans
Physical Characteristics
- Characterised by:
- Strong westerly winds
- Intense storms
- Extreme cold temperatures
- Pronounced seasonal variations
- Dominated by the Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC):
- Longest, strongest, and deepest-reaching ocean current on Earth
- Flows uninterrupted around Antarctica
Geological Formation
- Formed when Antarctica and South America drifted apart
- Creation of the Drake Passage enabled the development of the ACC
- This isolation cooled Antarctica and influenced global ocean circulation
Biodiversity and Productivity
- Cold, oxygen-rich, and nutrient-dense waters
- Supports:
- Krill
- Whales
- Seals
- Penguins
- One of the most productive marine ecosystems globally, despite extreme conditions
Role of the Southern Ocean in the Global Climate System
Carbon Sink Function
- Absorbs a large proportion of anthropogenic CO₂
- Cold waters enhance gas solubility, increasing carbon uptake
- Helps slow atmospheric accumulation of greenhouse gases
Heat Regulation
- Takes up vast amounts of excess heat generated by global warming
- Delays surface warming, acting as a thermal buffer
Ocean Circulation
- Drives global thermohaline circulation
- Connects major ocean basins, redistributing heat, salt, and nutrients worldwide
Sea Ice Dynamics
- Seasonal formation and melting of sea ice:
- Influences albedo (reflection of solar radiation)
- Regulates ocean-atmosphere heat exchange
- Impacts global weather and climate patterns
Emerging Concerns
- Warming may reduce the ocean’s carbon absorption capacity
- Changes in wind patterns could alter the Antarctic Circumpolar Current
- Ocean acidification threatens marine biodiversity
- Potential feedback loops could accelerate climate change
Significance for India and the World
- Slowing global warming benefits climate-vulnerable countries, including India
- Impacts:
- Monsoon systems
- Sea-level rise
- Extreme weather events
- Reinforces the need for:
- Global climate cooperation
- Protection of polar and ocean ecosystems
FAQs
Q1. Why is the Southern Ocean important for climate regulation ?
It absorbs large amounts of heat and carbon dioxide, slowing global surface warming.
Q2. What is the Antarctic Circumpolar Current ?
It is the world’s strongest and longest ocean current, circulating around Antarctica.
Q3. How does the Southern Ocean differ from other oceans ?
Its uninterrupted circulation, extreme conditions, and high carbon uptake make it unique.
Q4. What is the Drake Passage ?
A narrow sea passage between South America and Antarctica that enabled formation of the Southern Ocean current system.
Q5. Why is the Southern Ocean relevant for UPSC exams ?
It links physical geography, climate change, oceanography, and environmental conservation, making it important for both Prelims and Mains.
|



