(Preliminary Examination: Current Affairs)
(Mains Examination, General Studies Paper 3: Environmental Pollution; Science and Technology – Developments and Applications and Their Impact on Everyday Life.) |
Context
Air pollution in Delhi and North India reaches dangerous levels every winter. Recently, "cloud seeding" has been proposed as a potential solution to this crisis. However, from a scientific perspective, this approach is neither sustainable nor practical.
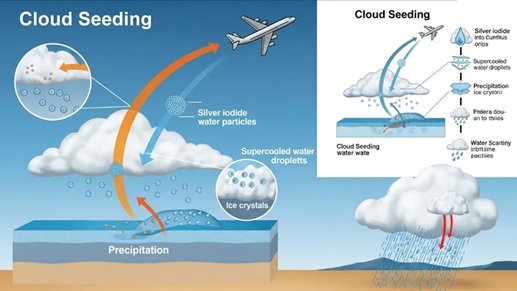
Cloud Seeding Meaning
- Cloud seeding is a scientific technique that attempts to artificially induce rain in the atmosphere.
- Silver iodide, sodium chloride, or other chemicals are released into the air to condense water vapor in clouds, producing rain.
- Its purpose is to increase rainfall in dry areas, alleviate water scarcity, or create artificial rain to reduce pollution.
- However, this technique can only be effective when there are sufficient clouds and moisture in the atmosphere.
Delhi's Air Pollution Problem
- Delhi's air quality remains poor year-round, but it reaches extremely dangerous levels in winter.
- When dry northwesterly winds blow after the monsoon, pollutants become trapped near the ground.
- Cold winds and weak air currents prevent pollution from dispersing, causing the air to become stagnant and heavy.
- During this period, the air has low humidity and no clouds form, making it difficult to induce artificial rain.
Main Causes
- Vehicular emissions
- Smoke from industrial units and thermal power plants
- Dust from construction activities
- Open burning of garbage and biomedical waste
- Stubble burning in Punjab and Haryana
- Unfavorable atmospheric conditions during winter
Application of Cloud Seeding
- The Delhi government has recently considered a cloud seeding plan to alleviate pollution.
- The idea is that artificial rain will wash away pollutants in the air and improve the AQI (Air Quality Index).
- However, scientifically, its effect is very short-lived; a maximum of a day or two.
- It requires the presence of clouds and appropriate atmospheric conditions, which are often absent in winter.
Challenges
- Scientific limitations: Cloud seeding is only possible when sufficient clouds and moisture are present.
- Limited impact: Pollution relief is temporary; the situation returns after a day or two.
- Environmental risks: Continuous use of chemicals like silver iodide can pollute soil and water sources.
- Lack of accountability: Who will take responsibility if heavy rainfall after cloud seeding leads to flooding?
- Waste of resources: This is an expensive technology that can waste public money for temporary results.
Other options
- Vehicle emission control: Promote public transport and encourage electric vehicles.
- Agricultural reform: Use of alternative technologies for stubble management.
- Industrial pollution control: Tighten emission standards in industrial units.
- Waste management: Ban open burning of garbage and strengthen solid waste management systems.
- Green belts and urban planning: Increase green cover and control construction activities.
- Sustainable energy: Use of clean energy sources instead of coal-fired power plants.
The Way Forward
- Long-term and scientific solutions are essential, rather than relying on glamorous technologies like cloud seeding.
- The government should focus on robust emission control policies, sustainable urban planning, and public awareness.
- Fighting pollution is not a technological experiment but a process of sustained policy and social cooperation.
- The real solution is “source control,” not “treating the symptoms” with temporary measures.
Conclusion
The solution to Delhi's air crisis lies not in experiments like cloud seeding, but in strong policy resolve, technological improvements, and citizen responsibility. Only a long-term and scientific approach can provide Delhi with clean air.



