- Recently, the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) achieved a major milestone under India’s hypersonic missile programme.
- DRDO successfully conducted a ground test of a full-scale, actively cooled, long-duration scramjet engine.
- This achievement significantly strengthens India’s position in advanced hypersonic technologies and paves the way for the development of future Hypersonic Cruise Missiles (HCMs).
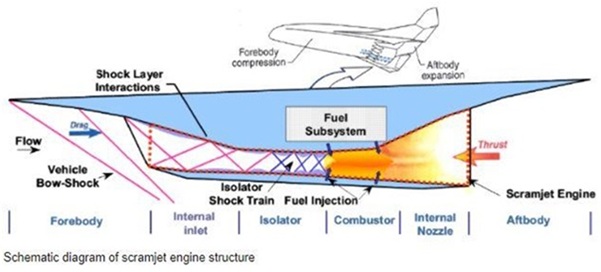
What is a Scramjet Engine ?
A Scramjet (Supersonic Combustion Ramjet) is an air-breathing engine designed to operate efficiently at hypersonic speeds (Mach 5 and above).
It is fundamentally different from conventional jet engines because it does not use rotating compressors or turbines.
Key Features
- The scramjet uses the vehicle’s extremely high speed to compress incoming air naturally.
- Supersonic combustion takes place inside the engine, meaning the airflow remains faster than the speed of sound even in the combustion chamber.
- This feature makes scramjets ideally suited for hypersonic cruise missiles.
- Typically, liquid hydrogen is used as fuel, while oxygen is drawn directly from the atmosphere, eliminating the need to carry an oxidiser.
- Scramjets offer much higher fuel efficiency compared to turbojet and ramjet engines at hypersonic speeds.
India has become the fourth country in the world to successfully demonstrate scramjet engine flight testing, highlighting its growing technological capability.
Working Principle of a Scramjet Engine
A scramjet engine operates in a sequential manner:
1. Air Intake
- A scramjet functions only when the vehicle is already flying at supersonic speed (around Mach 3 or higher).
2. Compression
- Due to the vehicle’s very high speed, incoming air is automatically compressed, eliminating the need for mechanical compressors.
3. Combustion
- Hydrogen fuel is injected into the compressed air.
- Combustion occurs while the airflow remains supersonic, which is the defining characteristic of a scramjet engine.
4. Thrust Generation
- The high-temperature, high-pressure gases produced by combustion are expelled rapidly through the exhaust.
- According to Newton’s Third Law of Motion, this generates extremely high forward thrust.
- Since a scramjet cannot produce thrust at zero speed, a rocket booster is required to accelerate the vehicle to the necessary initial speed.
What are Hypersonic Missiles ?
- The term hypersonic refers to objects that travel at Mach 5 (five times the speed of sound) or higher.
- Due to their extreme speed, reduced reaction time, and high manoeuvrability, hypersonic missiles are considered game-changers in modern warfare.
Types of Hypersonic Weapons
1. Hypersonic Glide Vehicles (HGVs)
- Launched using a rocket, similar to ballistic missiles.
- After re-entering the atmosphere, they glide at hypersonic speeds towards the target.
2. Hypersonic Cruise Missiles (HCMs)
- Powered by scramjet engines throughout their flight.
- They can fly at low altitudes and change direction, making interception extremely difficult.
Subsonic, Supersonic and Hypersonic Speeds
- Subsonic: Below the speed of sound (Mach < 1) — Passenger aircraft
- Supersonic: Faster than sound but below Mach 5 (Mach 1–5) — Fighter jets, BrahMos missile
- Hypersonic: Mach 5 or higher (Mach ≥ 5) — Hypersonic missiles
Importance of Scramjet Technology for India
- Strategic Advantage: Hypersonic weapons enhance India’s deterrence and national security capabilities.
- Indigenous Capability: This achievement strengthens the vision of Atmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliant India) in defence technology.
- Future Platforms: Scramjet technology can also be applied to future space launch systems and advanced military aircraft.
- Global Power Balance: It places India alongside the United States, Russia, and China in this cutting-edge technological domain.



