Food Irradiation
Food irradiation is a safe, scientifically validated food-processing technology in which food items are exposed to controlled amounts of ionizing radiation to preserve them. The objective is to enhance food safety, increase shelf life, and control pests and pathogens. Reputed global organizations such as the American Medical Association (AMA), FAO, WHO, and IAEA have already declared this technology safe.
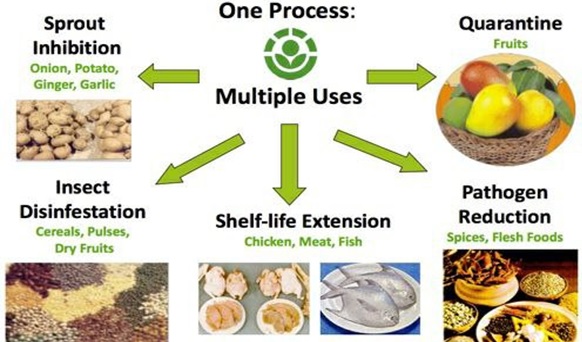
What is Food Irradiation?
It is a physical process in which food materials—fresh produce, grains, spices, seafood, meat—are treated with pre-determined radiant energy.
Objectives
- Increase the shelf life of foods
- Control or eliminate pests and pathogenic microorganisms
- Prevent parasitic infections
- Prevent sprouting (e.g., potatoes, onions)
- Slow down ripening of fruits and vegetables
- Reduce food-borne diseases
It is considered similar to other preservation techniques like microwaving and pasteurization.
How Does This Technology Work?
When ionizing radiation interacts with food, two types of processes occur:
(A) Primary Processes
- Energy + food → formation of ions and excited molecules
- Breakage in DNA and cellular structures → pests/microbes destroyed
(B) Secondary Processes
- Reactions between the primary products
- Influenced by:
- Moisture content of food
- Presence of oxygen
- pH
The compounds formed in these reactions are called radiolytic products. Scientific studies show these changes are extremely minimal and do not harm human health.
Importance of Radiolysis
- Water molecules break into free radicals
- These free radicals damage microbial DNA
→ Microorganisms and pests become inactive or are destroyed.
Advantages of Food Irradiation
(1) Improved Food Safety
- Destroys pathogens like E. coli, Salmonella, Listeria.
(2) Maintains Food Quality
- Taste, color, aroma, and nutrients remain largely intact.
(3) Pest Control (Disinfestation)
- Eliminates pests from grains, pulses, spices
→ Facilitates export/import.
(4) Processing Efficiency
- Highly effective when combined with cold storage or refrigeration.
(5) Alternative to Chemical Treatments
- Safe alternative to methods like sulfur fumigation.
Is Food Irradiation Safe?
Scientific consensus: The technology is safe.
Approved by:
- WHO
- FAO
- IAEA
- American Medical Association
- Codex Alimentarius Commission
Scientific Findings
- Food does not become radioactive
- No evidence of toxicity, cancer risk, or nutrient loss
- Used safely worldwide for over 50 years
Types of Radiation Used in Food Irradiation
(A) Gamma Rays
- Source: Cobalt-60 (Co-60)
- Deep penetration capability
- Suitable for large-scale food processing
- In India, BRIT supplies Co-60.
(B) X-Rays
- Produced by hitting high-energy electron beams on a metal target
- Suitable for packaged foods
- Also used in industrial and pharmaceutical sectors.
(C) Electron Beam (e-Beam)
- High-energy electrons from accelerators
- Low penetration → ideal for surface or small packages
- Fast processing.
Food Irradiation in India
Institutional Framework
- Department of Atomic Energy (DAE)
- BRIT – supplies Cobalt-60
- Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC) – R&D, technology development
- Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) – regulation
Policy Support
PMKSY (Pradhan Mantri Kisan SAMPADA Yojana)
- Supports establishment of multi-product irradiation units
- Part of "Integrated Cold Chain & Value Addition Infrastructure"
Status (As of August 2025)
- 16 project proposals approved
- 9 units operational
- Uses: spices, grains, onions-potatoes, seafood, fruits & vegetables
Major Irradiation Facilities in India
- KRUSHAK (BARC, Lasalgaon) – spices, onions
- Vashi Irradiation Facility (Navi Mumbai)
- Radiant Food Irradiation Plants (Private sector)
Challenges
- Lack of consumer awareness
- Unnecessary fear due to the word “radiation”
- High initial investment
- Limited commercial facilities
- Transportation and logistical issues
Global Perspective
- Widely used in the USA, France, Netherlands, China
- Key technology for spices, meat, fruits & vegetables trade
- Codex Alimentarius Commission has established global standards
Conclusion
Food irradiation is a scientific, safe, and environmentally friendly technology that can significantly improve food safety, agricultural exports, and supply-chain efficiency in India. With government support through PMKSY, its acceptance and application in India are steadily rising.




