What is the Exposome ?
The Exposome is an emerging scientific concept that refers to the totality of environmental exposures a person experiences throughout life — from conception to death — and how they influence health.
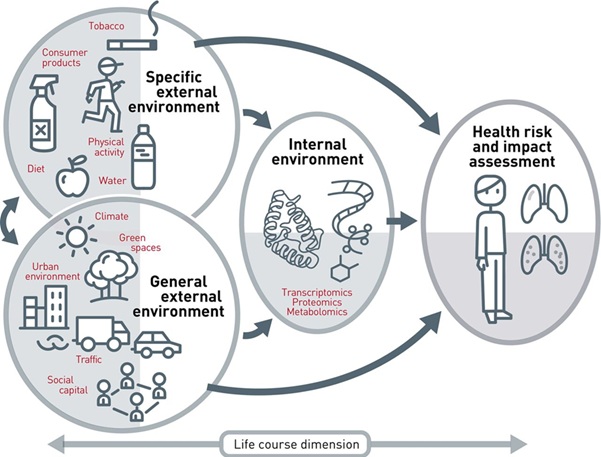
It complements the idea of the genome:
- Genome → genetic factors
- Exposome → environmental & non-genetic factors
The term was proposed in 2005 by epidemiologist Christopher Wild.
According to the International Human Exposome Network (IHEN), the exposome is: “the integrated collection of all physical, chemical, biological and psychosocial factors and their interactions affecting human health across the lifespan.”
In simple terms: While genes load the gun, the exposome pulls the trigger.
Components of the Exposome
The exposome has two broad categories: external exposures and internal exposures.
1. External Exposures
These come from the surrounding environment.
a) Environmental Factors
- Air pollution (PM2.5, ozone)
- Water contamination
- Soil chemicals
- Radiation
- Noise pollution
b) Chemical Exposures
- Pesticides
- Plastic chemicals (e.g., BPA, phthalates)
- Heavy metals (lead, mercury, arsenic)
- Industrial emissions
c) Biological Agents
- Bacteria
- Viruses
- Allergens (pollen)
- Microorganisms
d) Psychosocial Factors
- Stress
- Poverty & inequality
- Urbanization
- Workplace pressure
2. Internal Exposures
These occur within the body in response to external exposures.
- Metabolism (biochemical reactions)
- Microbiome (gut bacteria affecting immunity & nutrition)
- Inflammation & oxidative stress
- Lifestyle factors (diet, smoking, alcohol, physical activity)
These exposures accumulate across life and interact with genes to determine disease susceptibility.
Importance of the Exposome & Link with Diseases
Research suggests:
- 70–80% of diseases are influenced by environmental factors
- 20–30% by genetics
Thus, the exposome fills the gap left by genome-only research.
Major Diseases Associated
|
Exposure
|
Possible Disease Outcome
|
|
Air pollution
|
Asthma, COPD, lung cancer
|
|
Heavy metals
|
Neurological disorders
|
|
Poor diet
|
Obesity, diabetes
|
|
Chronic stress
|
Heart disease, depression
|
|
Early-life exposure
|
Lifelong cognitive impairment
|
Examples
- High PM2.5 levels → respiratory illness
- Childhood lead exposure → reduced adult cognitive ability
- Social inequality → chronic disease risk
Policy relevance
- Enables personalized prevention
- Supports wearable health monitoring
- Helps preventive public health strategies
Exposomics: Methods of Study
Exposomics = scientific study of the exposome. It uses both internal and external assessment tools.
1. Internal Assessment (Biological response measurement)
Uses “-omics” technologies:
- Genomics
- Transcriptomics
- Proteomics
- Metabolomics
- Lipidomics
These identify biomarkers showing exposure effects.
2. External Assessment (Exposure measurement)
- Wearable sensors (air quality monitors)
- Environmental sampling
- Laboratory analysis
- Questionnaires & lifestyle surveys
- Satellite & geospatial data
Role of Technology
- Artificial Intelligence
- Big Data analytics
- Machine learning models
They help map complex exposure–disease relationships.
Global Efforts: Human Exposome Project
Scientists worldwide aim to map the Human Exposome, similar to the Human Genome Project.
Major Initiatives
1. International Human Exposome Network (IHEN) – 2023
- Global coordination platform
- Based on European Human Exposome Network
- Large-scale collaborative research
2. Human Exposome Project (HEP)
- Lifetime exposure mapping
- AI-driven medical insights
- Moves medicine beyond genetics
3. European Human Exposome Network (EHEN) – 2020–2025
- Focus on urbanization, workplace, mental health
4. EIRENE Infrastructure – 2021
- Pan-European exposome research system
Expected Impact
- Disease prevention
- Precision medicine
- Better environmental policies
Exposome in the Indian Context
India has a high environmental disease burden.
Key concerns:
- Severe air pollution
- Contaminated water
- Chemical exposure
- Rising non-communicable diseases (NCDs)
Environmental factors contribute significantly to public health problems.
Potential Benefits for India
- Pollution–health mapping
- Early disease prediction
- Targeted public health programs
- Integration into National Health Mission
- Rural–urban health disparity assessment
Current Status
Exposomics research is emerging in:
- Pollution mapping
- Risk assessment studies
- Environmental epidemiology
Challenges
- Data collection complexity
- Privacy and ethics concerns
- Limited infrastructure
- Funding constraints
Challenges & Future Directions
Challenges
- Complete lifetime exposure mapping is extremely difficult
- Ethical issues (data privacy)
- Standardization of measurement
- Cost and infrastructure
Future
- Wearable monitoring devices
- AI-driven health prediction
- Personalized preventive medicine
- Integration with national health systems


