(Preliminary Exam: Current Affairs)
(Main Exam, General Studies Paper 3: Achievements of Indians in Science and Technology; Indigenous Technology Development and Development of New Technologies) |
Context
- Currently, more than 65% of deaths in India each year are due to non-communicable diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and cancer. Older medicines only suppress the symptoms, not cure the root cause of the disease. Now, new technologies such as CRISPR, CAR-T cell therapy, and mRNA vaccines have proven that it is possible to eradicate disease at the genetic level.
- The Government of India has declared “Precision Biotherapeutics” as one of the six thrust areas in the BioE3 policy for the year 2024. This year, ImmunoACT launched India's first CAR-T cell therapy, NexCAR19, which costs 8-10 times less than international therapies.
What is Precision Biotherapeutics?
This is a new medical approach that creates a unique drug or treatment based on a patient's genetic information (DNA), protein status, and lifestyle. While standardized drugs are the same for everyone, precision drugs are tailored to each patient.
Key Tools
- Gene editing (CRISPR-Cas9): Repairing faulty genes by cutting them out
- mRNA therapy: Teaching cells to make the correct protein or stop making the wrong one
- CAR-T cell therapy: Removing a patient's immune cells, training them to recognize cancer and then reintroducing them
- Monoclonal antibodies: Lab-made proteins that attack specific targets
- Artificial intelligence: Predicting how a drug will work
Why is it needed in India?
- India has a lot of genetic diversity; the same drug may work in Punjab but may not in Kerala.
- Thalassemia, sickle cell anemia, and some types of cancer are prevalent in the Indian population.
- Foreign drugs are very expensive (30-40 crore rupees per dose) and cannot be used in India.
- The IndiGen and GenomeIndia projects have mapped the genomes of over 20,000 Indians; now they need to be used for treatment.
- In the future, treatment will shift from hospitals to “predictive and preventive.”
Current Situation in India
Government Initiatives
- The Department of Biotechnology (DBT) and BIRAC prioritized this in the BioE³ policy.
- Research is underway at IGIB Delhi, NIBMG Kalyan (West Bengal), and THSTI Faridabad.
Private Sector Pioneers
- ImmunoACT: India's first CAR-T therapy (costing just ₹4.2 million)
- 4baseCare: AI-based genetic testing for cancer.
- Biocon, Dr. Reddy's, Zydus: Working on biosimilars and gene therapy
- Bugworks: New antibiotics
- Immuneel: Immuno-oncology
Challenges
- Lack of clear legislation: CDSCO does not have separate regulations for gene therapy
- Expensive drugs: Still beyond the reach of the common man
- Lack of biomanufacturing: Most materials come from abroad
- Privacy of genetic data: Fear of misuse
- Lack of training: Doctors and scientists lack training in new technologies
Global initiatives
- US: 30+ gene-cell therapies approved, Zolgensma, Casgevy (first CRISPR therapy in 2023)
- China: More than 800 clinical trials underway
- Japan and Korea: Faster approval process
- Singapore: Emerging as a biomanufacturing hub
Way forward
- At CDSCO A separate "Gene and Cell Therapy Wing" should be established.
- A biobanking law should ensure data security and donor consent.
- Expensive gene therapies should be included in Ayushman Bharat.
- Establish 5-10 biomanufacturing parks across the country (like those proposed in Hyderabad, Bengaluru, and Pune).
- Establish a National Bioethics Committee to monitor genetic data and treatments.
- Teach genetics and biotech in simple language in schools and colleges.
Conclusion:
Precision biotherapeutics is not just a new technology, but a path to move India from "treatment after illness" to "prevention before illness." If India invests now, by 2030 we will not only be able to provide affordable treatment to our patients but also export affordable gene therapies to the world. This could become the strongest pillar of a self-reliant India and a developed India @ 2047.
Know this too!
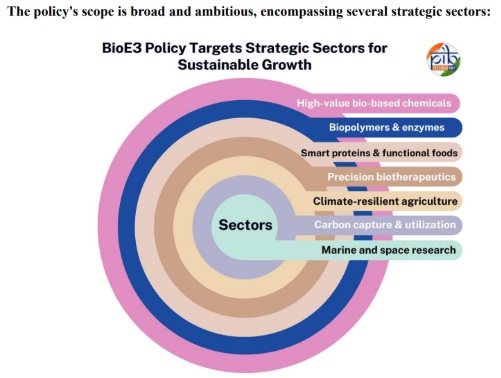
About the BioE3 Policy
- BioE3 stands for Biotechnology for Economy, Environment and Employment.
- Nodal Department: Department of Biotechnology (DBT) and Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC) to launch in 2024.
- Objective: To make India a global biotech hub, foster innovation, create jobs, and make emerging biotechnologies safe and accessible.
6 Key Focus Areas of the BioE3 Policy
-
Precision Biotherapeutics
- Promote gene therapy, cell therapy, mRNA treatments, monoclonal antibodies, and disease-specific targeted drugs.
- Develop personalized and targeted treatments based on genetic diversity in India.
-
Bio-manufacturing and Bio-foundries
- Increase indigenous production of biologics, vaccines, enzymes, and biomaterials on a large scale.
- Making India a low-cost global biomanufacturing hub.
- Enhancing collaboration between startups, industry, and research institutions.
-
Clean and Green Biotechnology
- Promoting environmentally friendly technologies such as biofuels, bioplastics, and bioremediation.
- Developing alternative bio-resources to reduce carbon emissions in industry and agriculture
-
Agricultural and Nutrition Biotechnology
- High-yield crops, pest-resistant seeds, biofertilizers, and biopesticides.
- Development of nutrient-rich (biofortified) crops.
- Promoting food security and climate-resilient agriculture.
-
Microbiome and One Health
- Treatments and diagnostics based on the microbiome of humans, animals, and the environment.
- Addressing antimicrobial resistance (AMR).
- Efforts to integrate health, environment, and veterinary medicine.
-
Biosecurity, Biosafety, and Emerging Technologies
- Developing regulatory frameworks for technologies such as gene editing, synthetic biology, and AI-biology.
- Strengthening biological hazard, pandemic risk, and lab safety standards.
- Ensuring safe and responsible use of biotechnology
|



