- Industries are often classified based on the level of pollution they generate and their impact on the environment.
- This classification helps regulatory bodies prioritize monitoring, enforce environmental norms, and promote sustainable industrial development.
- Among these classifications, White Category Industries represent the cleanest, least polluting segment of industries.
What Are White Category Industries?
- White Category Industries are those industries or business activities that have negligible or no adverse impact on the environment.
- They produce very low or zero pollution in terms of air, water, and land.
- Due to their minimal environmental footprint, these industries are exempted from rigorous pollution control regulations that apply to other industrial categories.
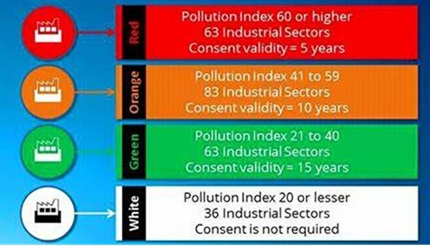
Classification of Industries Based on Pollution
The pollution-based industrial classification generally includes:
- Red Category: Highly polluting industries, such as chemical plants, thermal power stations, tanneries.
- Orange Category: Moderately polluting industries, like small-scale foundries, dye manufacturing.
- Green Category: Low polluting industries, such as food processing, textile mills with controlled emissions.
- White Category: Non-polluting or negligible polluting industries, including services and small manufacturing units.
Characteristics of White Category Industries
- Minimal or No Emissions: They do not emit harmful gases, particulates, or toxic effluents into the environment.
- No Hazardous Waste: These industries generate little to no hazardous waste or pollutants.
- Environmentally Friendly Processes: Use of clean technologies and eco-friendly raw materials.
- Limited Use of Chemicals: Operations avoid or minimize use of toxic chemicals.
- Low Water Usage and Wastewater Generation: These industries have limited water consumption and generate minimal or no wastewater.
Examples of White Category Industries
Some common examples include:
- Information Technology (IT) Services: Software development, IT consulting, data centres.
- Educational Institutions: Schools, colleges, coaching centres.
- Retail and Wholesale Trade: Shops, malls, showrooms.
- Handicrafts and Artisanal Work: Traditional crafts, handmade goods without chemical usage.
- Printing Services: Using non-toxic inks and minimal chemical solvents.
- Tailoring and Garment Stitching: Without large-scale dyeing or chemical treatment.
- Service Sector: Banking, finance, consulting, and other office-based industries.
- Repair and Maintenance Services: Electronic repair shops, vehicle repair without chemical waste.
Why Are White Category Industries Important?
- Environmental Protection: By identifying and promoting these industries, governments encourage sustainable development with minimal ecological damage.
- Regulatory Ease: Since these industries produce negligible pollution, they are exempted from stringent environmental clearances, reducing the compliance burden.
- Economic Growth: They facilitate industrial growth without compromising environmental health, striking a balance between development and conservation.
- Encouraging Clean Technologies: Highlighting these industries promotes the adoption of cleaner, greener technologies in the industrial sector.
- Focus on Polluting Industries: Helps regulatory agencies prioritize monitoring and actions for industries that cause more pollution.
Regulatory Implications
- White category industries do not require prior environmental clearance under many state pollution control board regulations.
- They are subject to simplified or minimal monitoring and reporting requirements.
- They encourage entrepreneurship by reducing delays and costs associated with environmental permits.
- Regulatory focus is shifted to Red and Orange category industries that pose significant environmental risks.
Impact on Sustainable Development
White category industries contribute significantly towards sustainable industrial growth by:
- Reducing the overall environmental burden.
- Promoting cleaner business models.
- Supporting the goals of climate change mitigation by limiting emissions.
- Providing employment opportunities with minimal ecological trade-offs.
Challenges and Considerations
- Monitoring: While these industries are low-polluting, ensuring they continue eco-friendly practices requires occasional monitoring.
- Transitioning Industries: Some industries might start as white category but may scale up, requiring reclassification and stricter controls.
- Awareness: Entrepreneurs should be educated about best practices to maintain their white category status.



