Prelims: (Environment & Ecology + CA)
Mains: (GS 3 – Environment; GS 2 – International Relations) |
Why in the News ?
The Global Methane Status Report 2025 warns that crop-residue burning is turning India into a global methane hotspot. The report highlights rising methane concentrations, increasing climate risks, and slow global progress toward mitigation commitments.
About the Global Methane Status Report

- Released by the UN Environment Programme (UNEP) and the Climate and Clean Air Coalition (CCAC).
- Tracks global progress on methane reduction.
- Assesses gaps in meeting the Global Methane Pledge, which aims to cut methane emissions significantly this decade.
Key Highlights of the 2025 Report
1. Methane Levels Rising Rapidly
- Atmospheric methane concentrations have more than doubled since pre-industrial times.
- Rising emissions are projected to cause:
- 24,000 additional premature deaths annually by 2030
- 2.5 million tonnes of crop losses each year
2. India’s Position
- India is the third-largest methane emitter in the world.
- Indian agriculture contributes 12% of global agricultural methane emissions, one of the highest shares globally.
- Crop residue burning, livestock emissions, and rice cultivation are major contributors.
3. Mitigation Potential
- Full implementation of NDCs and Methane Action Plans could reduce emissions by 8% by 2030.
- 72% of global methane mitigation potential lies within G20+ countries, which produce 65% of human-caused methane emissions.
What is Methane?
- Chemical Formula: CH₄
- A major component of natural gas
- Colorless, odorless, flammable, water-insoluble gas
- Also called marsh gas or methyl hydride
- Responsible for one-third of today’s global warming due to its high short-term warming potential (80x stronger than CO₂ over 20 years)
Impact on India
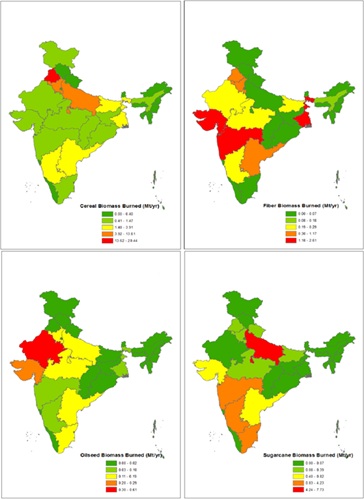
- Worsening air pollution from crop-residue burning
- Higher climate vulnerability: heatwaves, extreme rainfall
- Agricultural productivity losses
- Pressure on India to accelerate methane-mitigation policies
- Opportunity to lead global agricultural methane solutions
|
FAQs
Q.1: Why is methane reduction considered a quick-win for climate mitigation?
Ans: Methane has a short atmospheric lifetime (about 12 years) and a very high warming potential, so reducing emissions leads to rapid temperature decline, making it one of the fastest ways to slow global warming.
Q.2: Which sectors offer the highest methane mitigation opportunities globally?
Ans: Fossil fuels (oil, gas, coal), agriculture, and waste management offer the most cost-effective and scalable methane-reduction options.
Q.3: Why is India highlighted as a methane hotspot in the 2025 report?
Ans: Due to crop-residue burning, large-scale livestock emissions, and rice paddy methane release, combined with India’s high share of global agricultural methane emissions (12%).
Q.4: How does methane affect human health?
Ans: Methane contributes to the formation of ground-level ozone, which causes respiratory diseases, premature deaths, and worsens cardiovascular health.
Q.5: What role do G20+ countries play in global methane mitigation?
Ans: G20+ countries possess 72% of global methane mitigation potential because they emit 65% of global anthropogenic methane, making their cooperation crucial for meeting global climate targets.
|



