(Prelims: Current Affairs)
(Mains, General Studies Paper 2: Impact of Policies and Politics of Developed and Developing Countries on India's Interests; Overseas Indians.) |
Context
The impact of the additional tariffs imposed by the US on goods imported from India is clearly visible in the September 2025 export data. This move reflects America's trade protectionist stance, which has directly impacted the economies of many countries, including India.

US Tariff Impact: An Overview
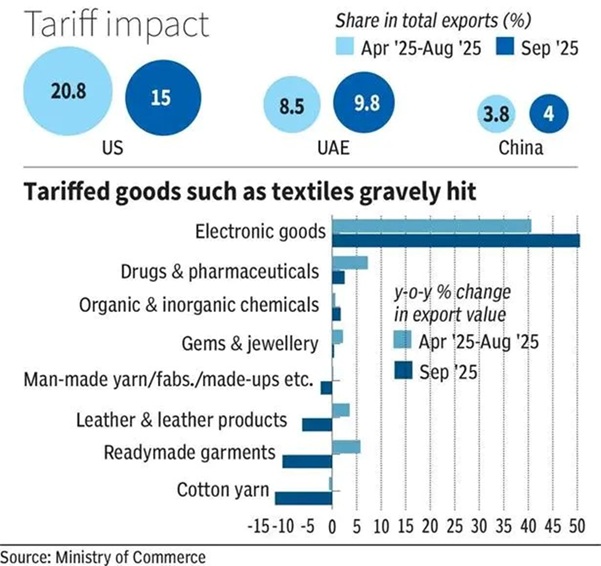
The US has imposed tariffs of up to 50% on Indian goods, negatively impacting India's exports. Export growth rates, particularly in traditional sectors such as textiles, gems and jewelry, and leather goods, have declined significantly.
Key Points
- India's exports to the US fell by 15% in September 2025, compared to 20% in April-August 2025.
- Textiles and readymade garments exports recorded an annual decline of 10.1%.
- Cotton yarn and fabric exports declined by 11.7%.
- Gems and jewelry growth slowed to a mere 0.4%.
- In contrast, electronic goods exports grew by 50.5%, particularly sharply in smartphone exports.
- Trump's tariff policy has begun to impact shrimp prices in the US market, with prices rising by 15-20%.
- India's share of supplies in the US shrimp market is approximately 45%, worth approximately $6 billion annually.
Impact on the Indian Economy
- Impact on employment: Millions of jobs in the textile, leather, and jewelry sectors could be affected.
- Trade imbalance: The US used to buy about a fifth of India's total exports, but this is now declining.
- Shifts in export markets: Indian exporters are now turning to alternative markets such as China, the UAE, Spain, and Bangladesh.
- Pressure on the manufacturing sector: Small and medium-sized exporters are losing competitiveness due to rising costs due to high tariffs.
Challenges
- Dependence on the US market: India's exports are still highly dependent on the US.
- Complexity of the global supply chain: Lower production costs in countries like China could weaken India's competitiveness.
- Domestic policy gaps: There are still many shortcomings in export promotion and logistics improvements.
- Currency fluctuations: The rupee's volatility against the dollar also impacts exports.
Way Forward
- Diversified market strategy: India should reduce its US dependence and expand into new markets such as Europe, Latin America, and Africa.
- Domestic production promotion: Production of high-value-added goods must be increased under the "Make in India" and PLI schemes.
- Trade Diplomacy: India should accelerate negotiations on tariff restructuring and a free trade agreement (FTA) with the US.
- Technology Investment: India's success in sectors such as electronics demonstrates that technology investment can offset tariff impacts.
Conclusion
US tariffs have dealt a blow to India's traditional export sectors, but they also provide an opportunity for India to make its export structure more diversified, modern, and competitive. India must focus on innovation, diversification, and trade balance as part of its long-term strategy to mitigate the impact of such policy shocks in the future.


