Why in News?
- The APEC Summit 2025 will be hosted by Gyeongju, South Korea, with the theme “Building a Sustainable Future.”
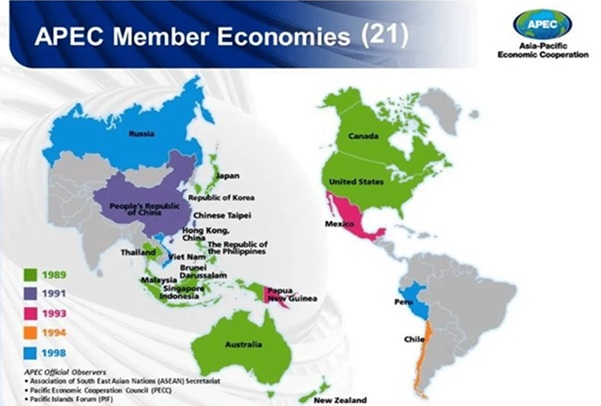
About APEC (Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation)
- Established: 1989
- Headquarters: Singapore
- Members: 21 economies, including the USA, China, Japan, Australia, Canada, and South Korea — together accounting for 60% of global GDP and 47% of global trade.
- Nature: APEC operates on a non-binding, consensus-based approach.
- Objective: To promote sustainable economic growth, free and open trade, investment, and regional cooperation.
- Key Focus Areas:
- Trade liberalization
- Digital economy
- Climate change
- Capacity building
Trade Tensions and Policy Uncertainty
- The US–China tariff war continues to affect regional trade.
- APEC Report 2025 projects:
- Regional GDP growth may decline to 2.6% (from 3.6% in 2024).
- Export growth: 0.4%, Import growth: 0.1%.
- Rising uncertainty due to the Trump administration’s tariffs and China’s restrictions on rare earth mineral exports.
Economic Growth and Inclusive Development
- The APEC region, representing 60% of global GDP, faces uneven growth amid global slowdown signals.
- Inflation is easing, but investment remains weak.
- 2025 Priorities:
- Transition to the formal economy (Lima Roadmap 2025–2040)
- Enhancing the participation of indigenous communities in economic development.
Digital Economy and Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- The APEC Internet and Digital Economy Roadmap (AIDER) concludes in 2025.
- New challenges emerging:
-
- AI ethics
- Data privacy and governance
- Bridging the digital divide
Climate Change and Sustainability
- Despite geopolitical tensions, climate issues remain central to APEC’s agenda.
- Continued emphasis on the Bangkok Goals on Bio-Circular-Green Economy (BCG Model).
- Key focus areas for 2025:
- Energy cooperation
- Food security
- Supply chain resilience
- Reports highlight sustainable growth as the foundation of regional cooperation.
Geopolitical Challenges
- Regional and global security concerns are influencing APEC dynamics.
- Major developments:
- Russia–Ukraine conflict
- Middle East unrest
- US–China strategic rivalry
- India and APEC
- India’s Status:
- Not a member of APEC but has shown consistent interest in joining since the early 1990s.
|
Year
|
Event
|
|
1991
|
India expressed interest in joining APEC.
|
|
1997
|
Formally applied for membership, but APEC imposed a moratorium on new members.
|
|
2007
|
Moratorium extended for another 10 years.
|
|
2012 & 2018
|
India renewed its interest, but no decision was made.
|
Reasons for India’s Non-Membership:
-
Geographical Criteria:
APEC limits membership to “Asia-Pacific” economies; India is often categorized under the “Indo-Pacific” region.
-
Pace of Economic Liberalization:
India’s market reforms in the 1990s were slower than APEC’s liberal economies.
-
China’s Opposition:
China reportedly resisted India’s entry to maintain its influence within APEC.
-
Moratorium Policy:
Since 1997, APEC has maintained a moratorium on new memberships.
Why APEC Matters for India:
1.Regional Economic Integration:
- APEC economies contribute ~60% of global GDP and ~48% of global trade.
- Membership would give India access to large, dynamic markets.
2.Boost to Trade and Investment:
- Reduced tariffs among members would benefit Indian exports.
3.Diplomatic Leverage:
- Provides a dialogue platform with major economies like the US, China, and Japan.
4.Economic Reforms:
- Membership could accelerate India’s trade facilitation, digital trade, and supply chain reforms.
India’s Current Strategy:
- Though not a full member, India participates as an Observer and in Partner Dialogue mechanisms.
- India is strengthening engagement through alternative platforms such as:
- BRICS
- Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF)
- QUAD
- RCEP (Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership) – indirectly connecting with APEC economies.
- Amid US tariff policies and shifting trade dynamics, India is pursuing bilateral trade agreements with key APEC members — notably the UK and Australia — to enhance market access and economic cooperation


