(Prelims: Important Days and Events)
(Mains, General Studies Paper 3: Achievements of Indians in Science and Technology; indigenous technology development and development of new technology) |
Context
World Television Day was organized by the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting and Prasar Bharati on November 21, 2025.

About World Television Day 2025
- World Television Day is celebrated every year on November 21. This day was declared by the United Nations General Assembly through a resolution passed in 1996.
- Its purpose is to honor television as an important medium of knowledge, information, education, and public opinion formation.
- Currently, approximately 900 million viewers watch television in India through more than 230 million TV homes, making it the most accessible and effective medium of communication in the country.
Evolution of Television in India
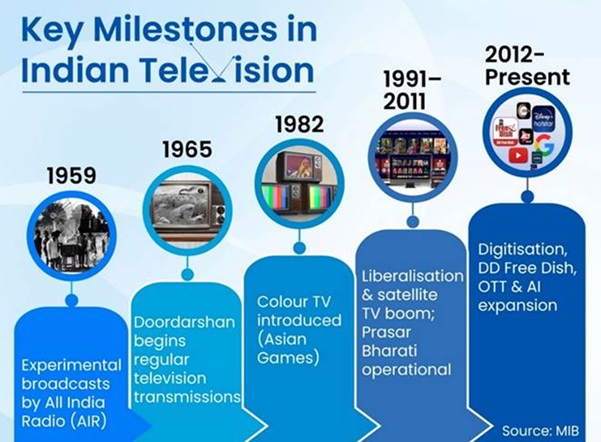
The journey of television services in India began as a small experiment in 1959 and today it is one of the largest broadcasting networks in the world. This development symbolizes the country's technological progress, digital transformation, and communications revolution.
- Initial and Experimental Phase (1959–1965)
- On September 15, 1959, testing of TV broadcasting began in Delhi with the support of UNESCO.
- The initial broadcasts focused on school education, rural development, and awareness programs.
- This service was entirely operated by All India Radio (AIR).
- Expansion and Institutional Development (1965–1982)
- Regular TV broadcasting began in 1965. During this period, Doordarshan evolved into an independent service.
- New TV stations were opened in several cities, including Mumbai, Srinagar, Amritsar, Kolkata, and Chennai.
- The SITE (Satellite Instructional Television Experiment) of 1975–76 was one of the world's largest educational broadcasting experiments.
- Through this experiment, programs on agriculture, health, family planning, and primary education were delivered to 2,400 villages.
- Color Broadcasting and National Reach (1982–1990)
- Color TV debuted with the 1982 Asian Games.
- By 1990, Doordarshan covered 70% of the population and 80% of the geographical area.
- Regional Doordarshan stations gave local languages and culture a prominent place in TV content.
- Liberalization and the Satellite Era (1991–2011)
- The 1990s saw the rise of private TV channels, such as Star TV (1991), Zee TV (1992), and Sony TV (1995).
- Entertainment, news, and film-based channels expanded rapidly.
- In 2004, DD Direct Plus (today's DD Free Dish) was launched, India's first free-to-air DTH service.
- In 1997, Prasar Bharati was formed, and Doordarshan and All India Radio gained autonomy.
- Digitization and Modern Broadcasting (2012–present)
- Cable TV digitization was completed between 2012 and 2017.
- DD Free Dish today reaches over 65 million households.
- Digital, HD, 4K, smart TV, and 5G technology have made TV more modern.
- India's TV network remains the most accessible media platform in the country.
Educational Initiatives
- Learning Support During COVID-19
- When schools were closed, Doordarshan became a primary medium for education.
- Classroom-based lessons broadcast on regional and national channels.
- PM e-Vidya Program
- 12 dedicated channels for classes 1–12 under the 'One Class – One Channel' (One Class – One Channel).
- Integration of digital content such as SWAYAM, DIKSHA, NCERT.
- SWAYAM Prabha
- 24×7 learning-based channel
- Learning content prepared by IITs, UGC, IGNOU, NCERT, etc.
India's Broadcasting Sector: Economy and Impact
- The media and entertainment sector contributed ₹2.5 trillion in 2024.
- The TV and broadcasting sector contributed approximately ₹680 billion.
- 918 private satellite channels (by 2025) India's multilingual and diverse TV landscape.
- TV plays a key role in education, health awareness, government schemes, and social development.
Technology and Innovation
Digital Terrestrial Television (DTT)
- High-quality signals, mobile reception, and spectrum efficiency
- Almost all Doordarshan analog transmitters have been phased out, except for 50 strategic locations
Expansion of DD Free Dish
- Increase from 59 channels in 2014 to 482 channels in 2025
- Both MPEG-2 and MPEG-4 formats available
- Wider reach in remote and border areas
|
What is MPEG
- MPEG (Moving Picture Experts Group) refers to global standards for digital video compression.
- MPEG-2 is used for standard-definition (SD) broadcasting on older set-top boxes.
- MPEG-4 provides higher efficiency and quality, supporting high-definition (HD) services.
- DD Free Dish uses both formats to ensure compatibility across devices and expand channel capacity.
|
New Regulatory Framework
- TRAI released recommendations for a new broadcasting authorization framework under the Telecommunications Act, 2023.
- Emphasis on OTT, multiplatform content, and improving quality standards.
Conclusion
India's television industry has currently entered a new era due to the digital revolution, new technologies, and multilingual content. From limited broadcasting in 1959 to reaching 900 million viewers today, it symbolizes India's information revolution, democratic dialogue, and inclusive communication. Television not only connects homes but also promotes education, awareness, cultural integration, and



