

| (Prelims: Important Personalities) |
On December 6, 2025, India observed the 70th death anniversary (Mahaparinirvan Diwas) of Dr. Bhimrao Ramji Ambedkar.
As Chairman of the Drafting Committee of the Constituent Assembly, he played a decisive role in the formulation of fundamental rights, a framework of equality, liberty, justice, and fraternity, a federal system, an independent judiciary, and protections for Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, and the underprivileged.
Dr. Ambedkar was not only the architect of the Constitution, but also the moral, social, economic, and democratic pillar of modern India. His message still reminds us that true progress lies in ensuring respect, equal opportunity, dignity, and justice for every individual. Even 70 years later, his ideology continues to influence both India's direction and future.
| (Prelims: Current Issues) |
A large number of flight cancellations and delays by IndiGo led to widespread dissatisfaction among passengers. On December 5, 2025, the DGCA granted IndiGo a temporary exemption from the new night-duty limit imposed on pilots. This move came amid persistent operational disruptions, crew shortages, and increasing passenger hardship.
Introduction: DGCA is India's statutory civil aviation regulatory body, whose primary objective is to ensure aviation safety, maintain airworthiness, and enforce regulations in line with global standards.
Establishment
Ministry
Objective
To promote safe, efficient, and reliable air transport, strengthening India's civil aviation sector in accordance with international (ICAO) standards.

Stage 1: End-of-Pipe (EP) Solutions
Major technologies:
Stage 2: CCUS-Compliant Design (CCD)
Expected benefits:
Stage 3: CCUS in One Pot (COP) – Integrated Emerging Technologies
Potential technologies:
1. Capture
CO₂ is captured from:
Types of capture:
2. Transport
Captured CO₂ is compressed and transported through:
3. Storage (Sequestration)
CO₂ is stored permanently in geological formations such as:
4. Utilisation
Captured CO₂ can be used as feedstock to produce:
1. Emission Reduction in Hard-to-Abate Sectors
2. Low-Carbon Power and Hydrogen Production
3. Negative Emissions (Removing CO₂ from Air)
BECCS provides true negative emissions because biomass absorbs CO₂ during growth and emissions are captured after combustion.
CCUS in India: Challenges and Opportunities
DST’s first CCUS R&D Roadmap provides a scientific and phased pathway that can help India:
CCUS is not the only solution, but it is an essential component of the net-zero strategy—especially in sectors where alternative green technologies are limited.
Food irradiation is a safe, scientifically validated food-processing technology in which food items are exposed to controlled amounts of ionizing radiation to preserve them. The objective is to enhance food safety, increase shelf life, and control pests and pathogens. Reputed global organizations such as the American Medical Association (AMA), FAO, WHO, and IAEA have already declared this technology safe.
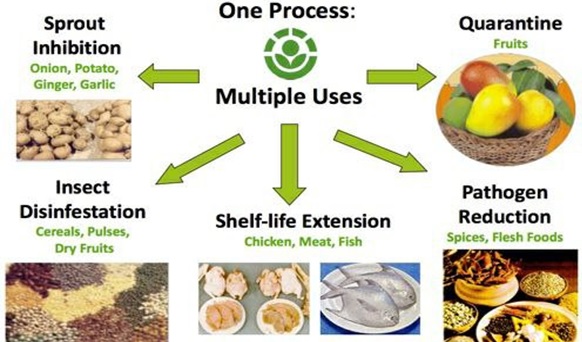
It is a physical process in which food materials—fresh produce, grains, spices, seafood, meat—are treated with pre-determined radiant energy.
It is considered similar to other preservation techniques like microwaving and pasteurization.
When ionizing radiation interacts with food, two types of processes occur:
(A) Primary Processes
(B) Secondary Processes
The compounds formed in these reactions are called radiolytic products. Scientific studies show these changes are extremely minimal and do not harm human health.
(1) Improved Food Safety
(2) Maintains Food Quality
(3) Pest Control (Disinfestation)
(4) Processing Efficiency
(5) Alternative to Chemical Treatments
Scientific consensus: The technology is safe.
Approved by:
Scientific Findings
(A) Gamma Rays
(B) X-Rays
(C) Electron Beam (e-Beam)
Institutional Framework
PMKSY (Pradhan Mantri Kisan SAMPADA Yojana)
Status (As of August 2025)
Major Irradiation Facilities in India
Food irradiation is a scientific, safe, and environmentally friendly technology that can significantly improve food safety, agricultural exports, and supply-chain efficiency in India. With government support through PMKSY, its acceptance and application in India are steadily rising.
| Prelims: (Labour Laws + CA) Mains: (GS-2 – Governance) |
A Private Member’s Bill titled the Right to Disconnect Bill, 2025 has been introduced in the Lok Sabha to legally protect employees from work-related calls, messages, or emails outside designated office hours.
The Bill, introduced by MP Supriya Sule, seeks to formally recognise an employee's right to disengage from official communication once working hours end. It aims to restore work–life balance in the increasingly digital and ‘always-on’ work environment created by remote and hybrid work.
The legislation highlights a growing global concern: employees being expected to respond instantly, even during personal time, weekends, and holidays.
1. Protection from After-Hours Communication
2. Creation of an Employees’ Welfare Authority
3. Mandatory Negotiation for Larger Workplaces
4. Overtime Compensation
5. Workplace Policies
Recent surveys cited in parliamentary discussions show:
The Bill aims to prevent burnout, improve mental health, and promote healthy workplace culture.
Countries like France, Italy, Ireland, Portugal, and Spain have already enacted right-to-disconnect laws. India’s Bill reflects evolving conversations about digital rights, privacy, and humane work environments.
(Note: Private member bills rarely become law, but are important for public and parliamentary debate.)
FAQs1. What is the Right to Disconnect ? It is the legal right of an employee to not respond to calls, texts, or emails after official working hours. 2. Does the Bill apply to all employees ? Yes, but companies with 10+ employees must formally negotiate after-hours norms. 3. Is this Bill likely to become law ? Most Private Member’s Bills are not passed, but they strongly influence policy discussions. 4. Why is such a law needed today ? Digital tools and hybrid work models have erased boundaries between work and personal life, leading to stress and burnout. 5. What happens if employees work after hours ? They must be paid overtime wages, and such work must be mutually agreed upon. |
| Prelims: (WHO + CA) Mains: (GS 2 – Governance; GS 3 - Health ) |
The World Health Organization (WHO) has officially declared Niger free of onchocerciasis (river blindness), making it the first country in the WHO African Region to eliminate the disease.
This achievement marks a historic milestone in the fight against neglected tropical diseases (NTDs).
Onchocerciasis has been a major public health challenge across Africa for decades, especially in remote, underserved communities. The disease is transmitted by blackflies breeding near rivers—often where agriculture, fishing, and daily life are concentrated—making eradication difficult.
Niger’s elimination is the result of:
Niger’s success proves that even vector-borne diseases entrenched in rural ecosystems can be eliminated with persistence.
Onchocerciasis is a parasitic infection caused by the filarial worm Onchocerca volvulus. It is transmitted to humans by the bite of infected Simulium blackflies, which breed in fast-flowing rivers and streams. Because transmission depends on the blackfly, the disease cannot spread directly from person to person.
This cycle keeps entire communities trapped in infection for generations.
WHO identifies it as one of the most neglected diseases, primarily due to geographic isolation and weak health infrastructure.
It is the second leading infectious cause of blindness worldwide, after trachoma.
1. Ivermectin (MDA Programmes)
The cornerstone of treatment is annual or biannual ivermectin, which:
2. Vector Control
Involves spraying to reduce blackfly populations, especially in high-transmission zones.
3. Community-based Distribution
Local volunteers and health workers play a key role in mass drug administration (MDA).
4. Rigorous Surveillance
Countries must demonstrate:
before WHO certifies elimination.
WHO considers this a “breakthrough moment for Africa’s NTD roadmap.”
FAQs1. What exactly is river blindness ? A parasitic disease caused by Onchocerca volvulus that affects the skin and eyes, leading to severe itching and blindness. 2. How did Niger eliminate the disease ? Through decades of mass ivermectin distribution, blackfly control, community-led programmes, and strong government–WHO coordination. 3. Does onchocerciasis spread from one infected person to another ? No. Transmission happens only through the bite of infected blackflies. 4. Which regions still have the disease ? Most cases remain in sub-Saharan Africa, with isolated pockets in South America. 5. What is the main treatment ? Annual or biannual ivermectin tablets administered to entire communities to break the transmission cycle. |
| Prelims: (Minority Affairs + CA) Mains: (GS-2 – Governance; GS-1 – Society) |
The Union Minister for Minority Affairs announced that the government will not impose penalties or strict action for the next three months on individuals or institutions that have not yet registered Waqf properties on the UMEED Portal, giving stakeholders additional time to complete documentation.
Waqf properties, historically created for charitable, religious, educational, and community welfare purposes, constitute one of the largest public endowment ecosystems in India.
However, for decades, the sector has faced recurring challenges:
An expert committee in 2013 and subsequent audits repeatedly highlighted the need for digitization, central monitoring, and transparent management of Waqf assets.
To address these concerns, the government introduced a framework for unified digital management, culminating in the creation of the UMEED Portal under the Unified Waqf Management, Empowerment, Efficiency and Development Act, 1995.
The portal aims to shift Waqf property governance from manual, fragmented records to centralized, real-time, transparent systems.
The Unified Waqf Management, Empowerment, Efficiency, and Development (UMEED) Portal is a centralized digital platform developed to modernize and streamline the management of Waqf properties across India.
It aims to:
The portal is managed by the Ministry of Minority Affairs, with registration facilitated through respective State Waqf Boards.
Legal Basis
1. Digital Inventory & Geo-Tagging
2. Real-Time Uploading & Verification
3. GIS Mapping Integration
4. Online Grievance Redressal
5. Transparent Leasing & Usage Tracking
6. Public Access to Verified Records
7. Rule on Women-Owned Properties
The Minister clarified that:
This aims to ensure smooth onboarding rather than coercive enforcement.
It marks a major shift from paper-based processes to digital governance.
FAQs1. What is the main purpose of the UMEED Portal ? To create a centralized digital system for registering, monitoring, and managing Waqf properties across India. 2. Why has the government paused penalties for three months ? To give stakeholders additional time to register and verify documentation without fear of punitive action. 3. Who manages the portal ? The Ministry of Minority Affairs, with support from State Waqf Boards. 4. Are women-owned properties considered Waqf ? No. Properties registered in the names of women are not eligible to be classified as Waqf properties. 5. How does geo-tagging help ? It accurately maps property boundaries, prevents illegal occupation, and creates reliable digital records. |
| Prelims: (Government Schemes + CA) Mains: (GS-3 – Economy) |
The Ministry of Food Processing Industries has reported significant progress under the Pradhan Mantri Formalisation of Micro Food Processing Enterprises (PMFME) Scheme, with major components showing substantial improvement as of 31 October 2025.
Launched on 29 June 2020, the PMFME Scheme is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme aimed at strengthening and formalising India’s vast network of micro-food processing enterprises.
It focuses on bringing traditional, unorganised, and small-scale food processing units into the formal economy, improving credit access, infrastructure support, branding, and standardisation.
The scheme seeks to build the overall capability and competitiveness of micro food enterprises through:
1. Enhanced Access to Credit
2. Integration Into Organised Supply Chains
3. Formalisation of 2 Lakh Units
4. Strengthening Common Services
5. Improved Access to Professional Expertise
1. Support for Individual Micro Enterprises
2. Support for FPOs, SHGs & Cooperatives
3. Institutional Strengthening
4. Project Management Framework
FAQs1. What is the main purpose of the PMFME Scheme ? To formalise and upgrade micro food processing units, enhancing credit access, infrastructure support, and market connectivity. 2. How many enterprises will be supported ? The scheme aims to formalise and assist 2 lakh micro enterprises across India. 3. What is the level of subsidy available for individuals ? Individual micro units receive 35% credit-linked subsidy, with a cap of ₹10 lakh. 4. Are SHGs eligible for seed capital ? Yes. SHGs receive ₹4 lakh per group as seed capital for member-level support. 5. What is ODOP and how is it linked to PMFME ? One District One Product (ODOP) promotes district-specific food products. New units under PMFME are supported only if they align with the district’s ODOP selection. |
| Prelims: (Nuclear Technology + CA) Mains: (GS 2 – International Relations; GS 3 – Security, Infrastructure) |
Russian President Vladimir Putin’s visit to India has renewed focus on the Kudankulam Nuclear Power Plant (KKNPP), as Russia accelerated fuel supply commitments and reiterated full support for completing India’s largest atomic energy project.
The Kudankulam announcements took place during the 23rd Annual India–Russia Summit, held in New Delhi in December 2025 — a key diplomatic mechanism that has continued since 2000 despite global geopolitical disruptions.
The 23rd Summit focused on:
The Summit reaffirmed that energy—particularly nuclear energy—remains the most durable pillar of India–Russia strategic relations.
Kudankulam, being the flagship nuclear project, became a central highlight of the discussions.
The Kudankulam project traces its origins to the 1988 India–USSR agreement, one of the last major deals signed before the Soviet collapse.
However, due to geopolitical upheavals and India’s nuclear isolation after the 1998 Pokhran tests, construction stalled for years.
The project regained momentum after the 2008 India–US Civil Nuclear Agreement, which opened the door for nuclear cooperation with international partners, including Russia.
Since then:
Putin’s 2025 visit marks the most significant push for the project since its inception.
President Putin, during his two-day visit to India, announced that the Kudankulam expansion is progressing rapidly and reaffirmed Russia’s strong backing for the project.
Russia’s state nuclear agency Rosatom recently delivered the first batch of nuclear fuel for Unit 3, marking a major milestone as the reactor moves closer to commissioning.
The fuel consignment was specially flown in from Russia, highlighting the priority Moscow attaches to the project.
“Two out of six reactor units have already been connected to the energy network, and four are still under construction. Achieving full power output will make an impressive contribution to India’s energy requirements.”
Alongside the existing collaboration, Putin also proposed cooperation in:
Reiterating Russia’s role as India’s “most dependable energy partner,” Putin assured continued supply of oil, gas, coal, and nuclear materials without disruption.
1. Strengthening the Southern Power Grid
Units 1 and 2 already supply 2,000 MW to Tamil Nadu and neighbouring states—easing peak load pressure and enabling reliable baseload electricity.
2. Boost to India’s Clean Energy Goals
3. Enhancing Energy Security
Long-term fuel supply agreements with Russia ensure stability and predictability in nuclear operations.
Broader Impact: Deepening India–Russia Strategic Energy Partnership
The project’s momentum highlights the alignment between India’s long-term energy planning and Russia’s strategic export priorities.
FAQs1. Why has Kudankulam returned to the spotlight ? Putin’s visit accelerated fuel supply and reaffirmed Russia’s commitment to completing all six units, fast-tracking the plant’s expansion. 2. What type of reactors does Kudankulam use ? It uses VVER-1000 pressurized light-water reactors supplied by Russia. 3. Which units are currently operational ? Units 1 and 2 are operational, while Units 3 to 6 are under construction. 4. Why is Kudankulam important for India’s energy sector ? It strengthens the southern grid, increases clean energy capacity, reduces fossil fuel dependence, and contributes to long-term energy security. 5. What new areas of cooperation did Putin propose ? Small Modular Reactors (SMRs), floating nuclear plants, and applications of nuclear technology in medicine and agriculture. |

Our support team will be happy to assist you!
